

Assume you are a market researcher of a company looking to introduce a new product to the market. You must collect data from a sample of potential customers as part of your research to determine their preferences and purchasing behavior. But how can you be sure that the information you get from your sample is accurate for all of the people who might buy your product? The idea of sampling error comes into play here.
It is the difference between what a sample has and what the entire population has. It can significantly affect how accurate and reliable market research data is.
We will cover ways to reduce sampling error in this article to get more accurate and reliable results. Now, grab your favorite coffee and get ready to explore what sampling error is.
A sampling error occurs when the sample used in the study does not represent the entire population. Although sampling errors occur frequently, researchers always include a margin of error in their conclusions as a matter of statistical practice.
The margin of error is the amount allowed for a miscalculation to represent the difference between the sample and the actual population.
Sampling is a type of analysis where a small sample of observations is chosen from a larger population. The selection bias process can produce both sampling errors and non-sampling errors.
Sampling errors are differences between a sample’s values and the actual population’s values. This is because a sample does not accurately represent the whole population of data.
Since there was a mistake in collecting the data, the results from sampling are no longer valid. Also, when a sample is chosen randomly or because of bias, it doesn’t represent the whole population, and sampling errors are likely to happen.
It is possible to avoid them if analysts carefully choose representative subsets of data from which to draw conclusions about the entire population. Factors including sample size and design, diversity in the population, and sampling percentage all contribute to sampling errors.
Diversity in the population increases the error in the estimations since it causes sampling to produce mixed results. Increasing the size of the samples allows them to represent the population more accurately, reducing the impact of population variation.
It is important to consider sampling errors before reporting survey results to establish confidence in the reliability of the estimates and their conclusions.
Here are the top four market research errors while sampling:
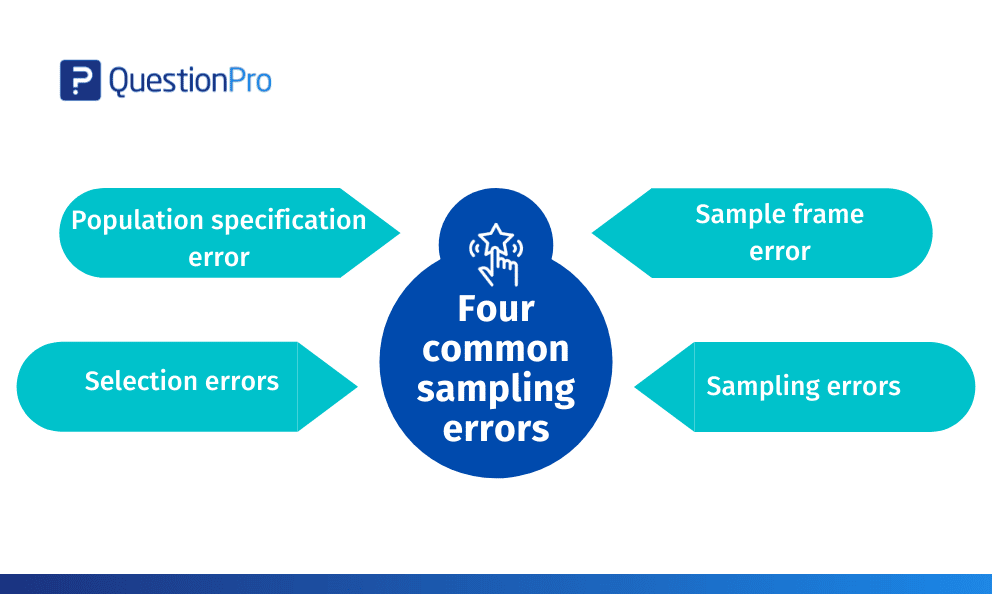
A population specification error occurs when researchers don’t know precisely who to survey.
Sampling frame error occurs when researchers target the sub-population wrongly while selecting the sample.
Selection error occurs when respondents self-select themselves to participate in the study. You can control selection errors by going the extra step to request responses from the entire sample. Only interested ones respond.
Sampling errors occur due to a disparity in the representativeness of the respondents. It majorly happens when the researcher does not plan his sample carefully.
LEARN ABOUT: Survey Sampling
Let’s look more closely at this example.
Let’s say a political party conducts a survey to find out how well-liked their candidate is before a major election. Instead of picking a random sample of the whole population to survey, they only ask their own members.
The sample would be skewed since party members may have extremely different opinions and tastes from the rest of the population. Party members may care more about their candidate’s ideals or be more loyal to them. This may cause the survey to suggest more support than the general population has.
Suppose the survey results are used to make campaign decisions, such as where to allocate money or which issues to prioritize. In that case, they may not accurately reflect the candidate’s support among the people. This could result in a poor campaign plan, affecting their election chances.
To avoid these kinds of sampling errors, it is essential to use a sampling method that is representative of the population being studied, such as random sampling or stratified random sampling, and to make sure that the sample size is big enough to give accurate results.
Statistical theories help researchers measure the probability of sampling errors in sample size and population. The size of the sample considered from the population primarily determines the size of the sampling error. Larger sample sizes tend to encounter a lower rate of errors.
Researchers use a metric known as the margin of error to understand and evaluate the margin of error. Usually, a confidence level of 95% is considered to be the desired confidence level.
Pro Tip: If you need help calculating your own margin of error, you can use our Margin of Error Calculator.
Surveys can have sampling and non-sampling errors. Survey findings can be affected by sampling and non-sampling mistakes.
Sampling error arises when a survey sample does not accurately represent the population being researched due to random sampling. Sampling and non-response bias, measurement error, and sampling variability can cause this.
Non-sampling error includes all survey errors other than sampling errors. This includes questionnaire design, coding, data input, data collection, processing, and analysis errors. Improper interviewer training, insufficient or inaccurate data, or data analysis or reporting errors can create non-sampling errors.
Non-sampling error can be decreased by applying quality control measures and ensuring that all components of the survey process are properly designed, implemented, and monitored. In contrast, sampling error can be reduced by utilizing appropriate sampling procedures and increasing the sample size.
We have published a blog that talks about subgroup analysis; why don’t you check it out for more ideas?
Sampling in statistics means choosing the research group. Sampling error and sampling bias affect sample accuracy and representativeness in statistics.
Sampling error occurs because a sample is a subset of the population and may not precisely represent it. Instead, sampling bias occurs when the sample is not representative of the population. This may happen if the method used to choose the sample favors or excludes particular sorts of people, resulting in an overrepresentation or underrepresentation of particular groups.
Using stratified or random sampling and unbiased, population-representative sample selection can reduce sampling bias. On the other hand, sampling error can be reduced by using the proper sampling methods and making the sample size bigger.
Sampling errors are easy to identify. Here are a few simple steps to reduce sampling error:

We have also created a tool to help you determine your sample size easily: Sample Size Calculator.
A sampling error is measurable, and researchers can use it to their advantage to estimate their findings’ accuracy and variance.
QuestionPro is survey software that includes a number of features and tools that can aid in the reduction of sampling errors. QuestionPro can assist in the following ways:
Researchers can use these features and tools to help cut down on sampling errors and make sure their samples are more accurate and representative.
Surveys are an extremely useful tool for both researchers and marketers. Introducing sample error can make research unreliable at best and dangerous at worst. Responding to misleading info can potentially ruin research or a business. So, be careful to avoid the sample errors that we have discussed.
Do you still worry about sampling errors? For your polls, surveys, and questionnaires, consider utilizing QuestionPro. Your surveys can be sent online, which will increase the sample size determination and response rates.
You may quickly and easily build surveys and add media to ensure that all participants can understand your surveys. So signup right away!